OLED intermediates serve as the core building blocks for synthesizing functional materials in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). They act as the critical link between basic chemical raw materials and end-use OLED functional materials (emissive layers, charge transport layers, host materials, etc.). Their production requires precise organic synthesis reactions and demands extremely high purity and structural regularity. Their structural design directly determines the optoelectronic performance of subsequent OLED functional materials, thereby influencing the display quality, lifespan, and power consumption of OLED panels. As the core upstream material in the OLED supply chain, they represent a high-value-added field at the intersection of fine chemicals and electronic materials.
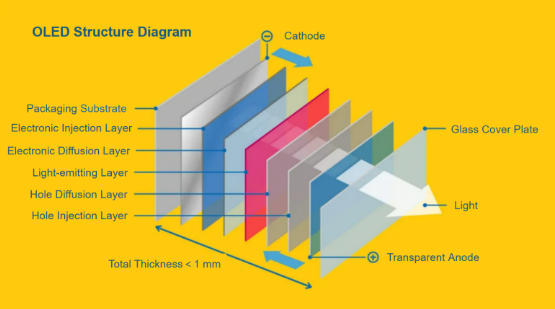
OLED intermediates are not single compounds but a class of organic compounds featuring specific functional groups or conjugated structures. They are not directly used in OLED device fabrication but can be assembled and modified through subsequent organic reactions—such as coupling, cyclization, substitution, and coordination—into various functional materials required for OLED devices. These include luminescent materials, hole-transporting materials, electron-transporting materials, host materials, and dopant materials. OLED intermediates serve as the “molecular building blocks” for OLED functional materials. By combining and modifying different building blocks, molecular structures of OLED functional materials meeting diverse performance requirements can be constructed.
The classification of OLED intermediates closely corresponds to the functional layers of OLED devices. Core classifications revolve around the synthesis requirements for three major functional material categories: charge transport, light-emitting, and host materials. Different types of intermediates exhibit distinct structural and functional group characteristics, all centered around aromatic rings or heterocyclic rings as core skeletons. Below are the six most mainstream categories of OLED intermediates in the industrial sector:
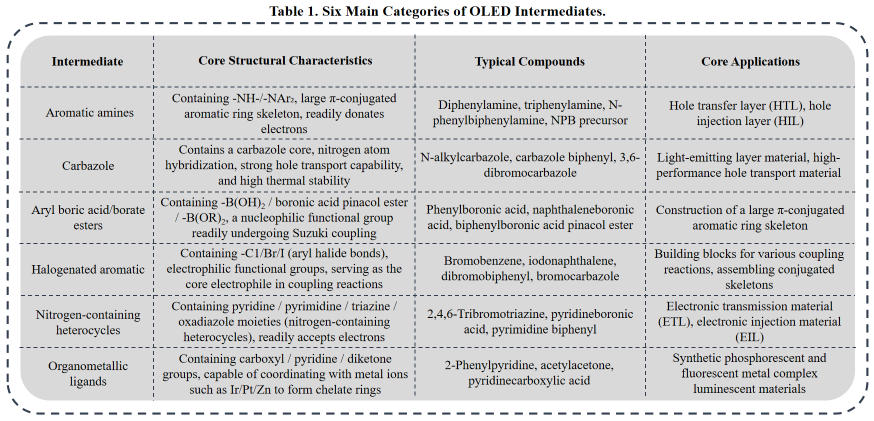
The stringent requirements for optoelectronic performance, lifespan, and stability in OLED devices dictate that intermediates must meet far higher performance standards than ordinary fine chemical products. Purity, structural regularity, thermal stability, and functional group activity are the four core metrics, with purity being paramount. Trace impurities can directly cause subsequent OLED functional materials to fail. Below are the mandatory industrial production standards:
Ultra-high purity (core)
General OLED intermediates: Purity ≥ 99.9% (HPLC), High-end OLED intermediates (e.g., phosphorescent ligands, triazine electron transport precursors): Purity ≥ 99.99% Strictly controlled levels of metal impurities, organic impurities, moisture, and residual solvents: Metal impurities ≤ 10 ppm (Palladium catalyst residues are a primary concern, causing dark spots in OLED devices) Moisture ≤ 500 ppm to prevent failure in subsequent syntheses like Grignard or lithiation reactions Residual solvents ≤ 100 ppm to meet environmental and safety requirements for OLED panels.
Structural Integrity
Substitution sites in OLED intermediates must be precisely positioned. Isomers represent one of the primary organic impurities and are difficult to remove through purification. For example, p-substituted and o-substituted biphenylboronic acids are isomers. If o-substituted impurities exist in the intermediate, the resulting functional material will exhibit distorted molecular structures that disrupt the π-conjugated system, significantly reducing charge transport rates and luminous efficiency.
Appropriate Functional Group Activity
Functional groups are central to intermediates' participation in subsequent synthesis reactions. Excessive activity leads to self-polymerization and side reactions, while insufficient activity results in low reaction yields and harsh reaction conditions.
Excellent Thermal Stability and Storage Properties
Intermediates must have a melting point/decomposition temperature ≥ 100oC to prevent thermal decomposition during subsequent synthesis steps (e.g., reflux, heating). Must remain stable for over 3 months under nitrogen protection, low temperature (0~25oC), and light-shielded conditions to prevent oxidation, hydrolysis, and deliquescence.
Low Volatility
The vapor pressure of intermediates must be sufficiently low to prevent yield reduction due to volatilization during subsequent OLED functional material synthesis. It also prevents residual volatile impurities from affecting the vacuum deposition process of OLED devices.
As OLED technology advances toward higher resolution, luminous efficiency, longevity, flexibility, and Micro OLED applications, downstream functional materials impose new demands on intermediate structures and performance. Concurrently, industrial imperatives for carbon neutrality and cost reduction drive process upgrades. Future OLED intermediate development will focus on four core directions: novel structural design, greener manufacturing processes, high-purity refinement, and integrated production layouts.

This is the first one.
Contact us to learn more about our advanced electronic chemicals and speciality polymer materials, and how they can enhance your production performances.